Table of Contents
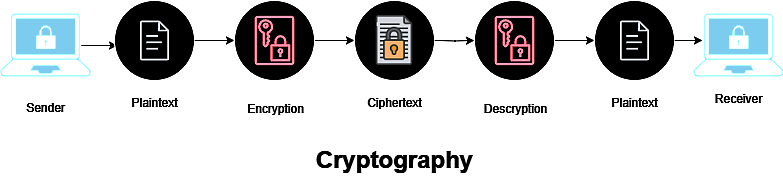
Cryptography is a technique for protecting communication and information, using codes to ensure that only the intended recipient can understand and interpret the information. Thus restricting the access of unauthorized information. “Crypto” is the prefix for “hidden” and “graphy” is the suffix for “writing”. Cryptography uses methods of information protection derived from mathematical ideas and a system of calculations based on rules or algorithms, which transform communications in ways that are difficult to decipher. These algorithms are used to protect cryptographic keys, digital signatures, data privacy protection, online surfing, and private transactions such as debit and credit card purchases.
Techniques used For Cryptography
In the modern era of computers, cryptography is often associated with the process of converting plain text into cipher text so that only the intended recipient can decode it, a process known as encryption. Decryption is the process of translating encrypted text into plain text.
Features Of Cryptography are as follows:
- Confidentiality: Information is confidential if it is available only to the person for whom it is intended and no one else.
- Integrity: Data cannot be added or changed while stored or transferred without the knowledge of the sender and the intended recipient.
- Non-reduction: The creator/sender of the information cannot withdraw its plans to transmit the information at a later time.
- Authentication: Identity of sender and receiver is verified. In addition, the origin and destination of the information are verified.
Types Of Cryptography:
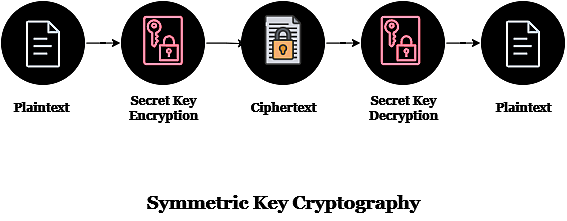
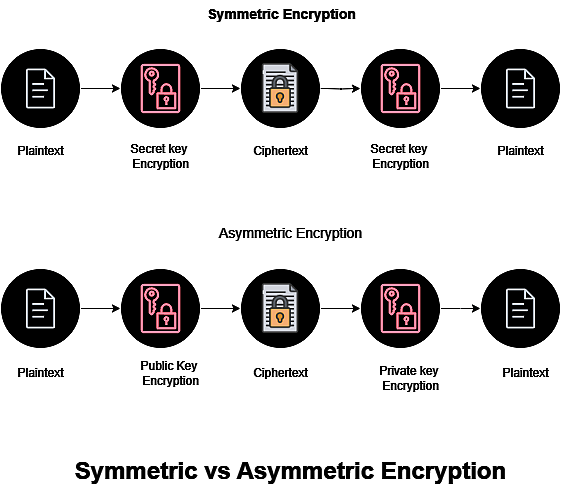
Symmetric Key Cryptography
With this encryption technique, communications are encrypted and decrypted using a single common key shared by both sender and receiver. Although symmetric key systems are fast and easy to use, there is one drawback: the sender and receiver must exchange keys in a secure way. The two most widely used symmetric key encryption systems are Data Encryption System (DES) and Advanced Encryption System (AES).
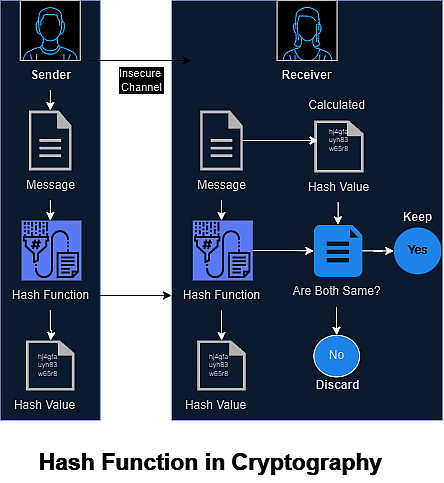
Hash Functions:
This algorithm does not use any key. Because the fixed-length hash value is calculated based on the plaintext, it is difficult to reconstruct the content of the plaintext. Hashing functions are used in operating systems to encrypt passwords.
Asymmetric Key Cryptography:
In this approach, data is encrypted and decrypted using a pair of keys. The encryption process uses the recipient’s public key, while the decryption process uses the recipient’s private key. Private keys and public keys are different. Only the recipient knows his private key, so even though the public key is available to everyone, he alone can decode it. The RSA algorithm is the most widely used asymmetric key encryption algorithm.
Applications Of Cryptography:
- Computer Passwords: A common use of cryptography in computer security is creating and maintaining passwords. The password is hashed and compared to the previously saved hash when the user signed in. Before being stored, passwords are encrypted and hashed. Using this method, passwords are encrypted so that they cannot be read by a hacker, even if they gain access to the password database.
- Digital Currencies: Cryptography is also used by digital currencies like Bitcoin to secure transactions and prevent fraud. Transactions are secured by complex algorithms and cryptographic keys, making it nearly impossible to tamper with or forge transactions.
- Secure Web Surfing: Users are protected from interception and man-in-the-middle attacks using cryptography, which is used in online browsing. To create a secure channel for communication, the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt data between web servers and clients using public key cryptography.
- Electronic Signature: Used to sign documents, an electronic signature is a digital version of a handwritten signature. Public key cryptography can be used to validate digital signatures created using cryptography. Electronic signatures are legally enforceable in many countries and their use is growing rapidly.
- Authentication: Cryptography serves as a means of authentication in a variety of contexts, including bank account access, computer logins, and secure network use. Authentication protocols use cryptographic techniques to verify a user’s identity and that they have the necessary access privileges to a resource.
- Cryptocurrencies: To protect transactions, prevent fraud, and maintain network integrity, cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum and Bitcoin rely heavily on cryptography. Transactions are secured by complex algorithms and cryptographic keys, making it nearly impossible to tamper with or forge transactions.
Advantages
- Access Control: Access control can be implemented using cryptography, to ensure that only people with proper authorization can access a resource. Thanks to encryption, only people with the correct decryption key can access the resource.
- Secure Communication: Cryptography plays an important role in ensuring secure Internet communication. It provides a secure method for sending sensitive data such as bank account numbers and passwords over the Internet.
- Attack Protection: Cryptography helps defend against various attacks, including replay and man-in-the-middle attacks. It provides tips on how to recognize attacks and how to thwart them.
Also read: How to Protect Yourself from a Rainbow Table Attack


1 thought on “Revealing the power of cryptography and its 3 dynamic forms”